ное. . 18, 2024 19:41 Back to list
china a gabion
The Role of Gabions in China’s Infrastructure and Environmental Management
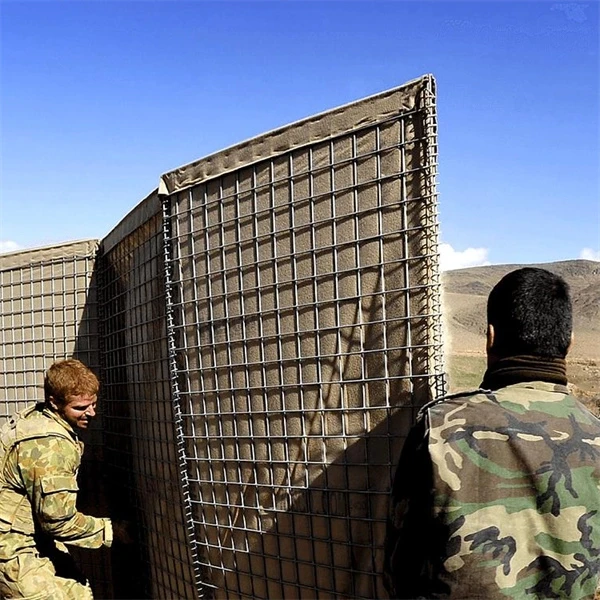
In recent years, the use of gabions has gained traction across various sectors in China, particularly in infrastructure development and environmental management. Gabions, which are wire mesh cages filled with rocks, stones, or concrete, serve multiple purposes, from erosion control to marine protection, flood management, and even architectural applications. This article explores the significance of gabions in China’s construction and environmental strategies and highlights their benefits and applications.
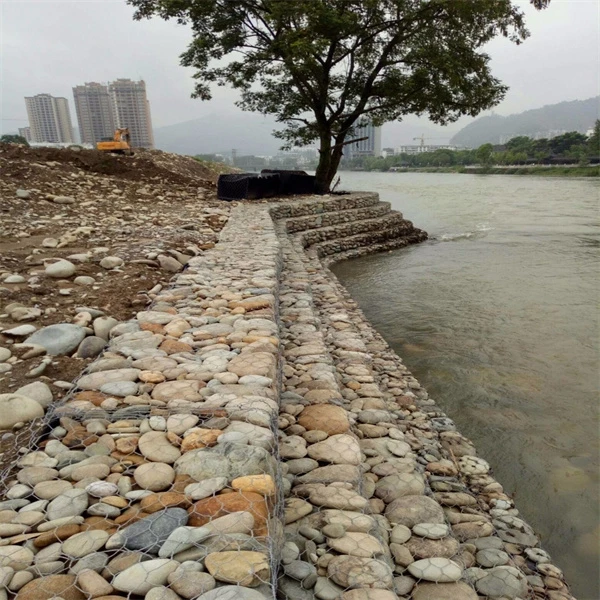
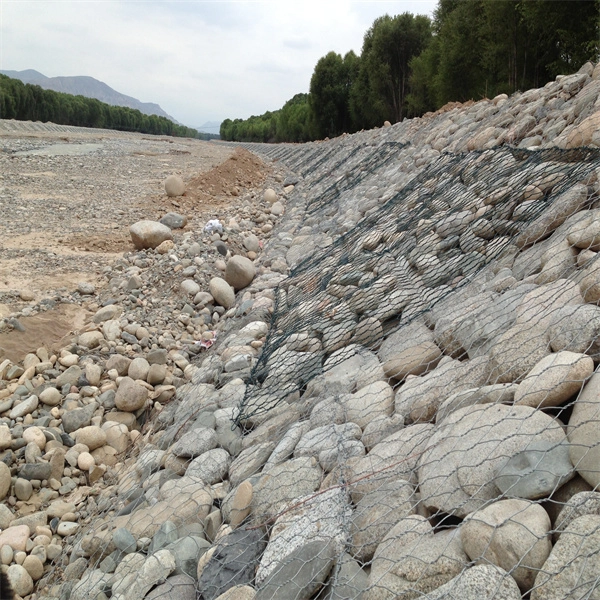
One of the primary uses of gabions in China is in controlling soil erosion, a severe issue due to rapid urbanization, deforestation, and climate change. The country's mountainous regions, in particular, suffer from landslides and runoff that threaten communities and agricultural land. Gabions provide a sustainable solution by stabilizing slopes and riverbanks. They absorb and dissipate energy from rainfall and flowing water, reducing the speed of water movement and allowing sediment to settle. This protective mechanism is valuable for safeguarding agricultural fields and preventing property damage in nearby settlements.
The Role of Gabions in China’s Infrastructure and Environmental Management
Another significant application of gabions in China is in the field of environmental restoration. As part of ecological restoration projects, gabions have been used to rebuild habitats and stabilize riverbanks, contributing to biodiversity conservation. For instance, in areas where natural vegetation has been destroyed, gabions provide a framework for planting native flora, aiding in the rehabilitation of ecosystems. Over time, these structures integrate with surrounding environments, promoting natural habitat for various wildlife species.
china a gabion
Gabions are also finding their place in architectural and urban design. In modern urban planning, they are often used to create aesthetically appealing features, such as walls, fences, and seating areas in parks or public spaces. Their versatility allows architects to incorporate them into innovative designs while maintaining functionality. Over the years, gabion walls have gained popularity for their rustic look and environmentally friendly nature, blending seamlessly with natural landscapes.
The advantages of gabions extend beyond their functional applications. They are cost-effective, as the materials used for filling them—such as local stones—are often readily available and inexpensive. Furthermore, gabions are durable and require minimal maintenance. Unlike traditional concrete structures, they can adapt to changes in the landscape and are less likely to crack under pressure or environmental stress.
Moreover, gabions have positive environmental impacts due to their ability to promote natural drainage and vegetation growth. They can act as habitats for small animals and insects, supporting local biodiversity. Additionally, the use of native stones and vegetation helps maintain the region's ecological balance, fostering resilience against climate-related challenges.
In summary, gabions represent a versatile and effective tool in tackling some of China’s pressing infrastructure and environmental issues. Their applications in erosion control, flood management, ecological restoration, and urban design showcase their multifaceted benefits. As China continues to face the challenges posed by rapid urbanization and climate change, the strategic implementation of gabions will be essential in promoting sustainable development and ensuring the safety and resilience of its landscapes and communities. With their economical and ecological advantages, gabions are likely to play an indispensable role in China’s future infrastructure and environmental management endeavors.
-
Why PVC Coated Gabion Mattress Is the Best Solution for Long-Term Erosion Control
NewsMay.23,2025
-
Gabion Wire Mesh: The Reinforced Solution for Modern Construction and Landscape Design
NewsMay.23,2025
-
Gabion Wall: The Flexible, Seismic-Resistant Solution for Modern Landscaping and Construction
NewsMay.23,2025
-
Gabion Wall Solutions: The Durable, Decorative, and Affordable Choice for Every Landscape
NewsMay.23,2025
-
Gabion Basket: The Durable and Flexible Alternative to Traditional Retaining Walls
NewsMay.23,2025
-
Gabion Basket: The Proven Solution for Slope Stability and Flood Control
NewsMay.23,2025
-
Versatility of Chain Link Fence Gabion
NewsMay.13,2025






