nov . 14, 2024 22:57 Back to list
gabion rock factory
The Significance of Gabion Rock Factories in Modern Construction
The construction industry has witnessed a significant transformation over the years, driven by the need for innovative materials and sustainable practices. One such advancement is the use of gabions—wire mesh cages filled with rocks, often used for retaining walls, erosion control, and other structural applications. Gabion rock factories play a pivotal role in the production of this versatile construction material, and their importance cannot be overstated.
What are Gabions?
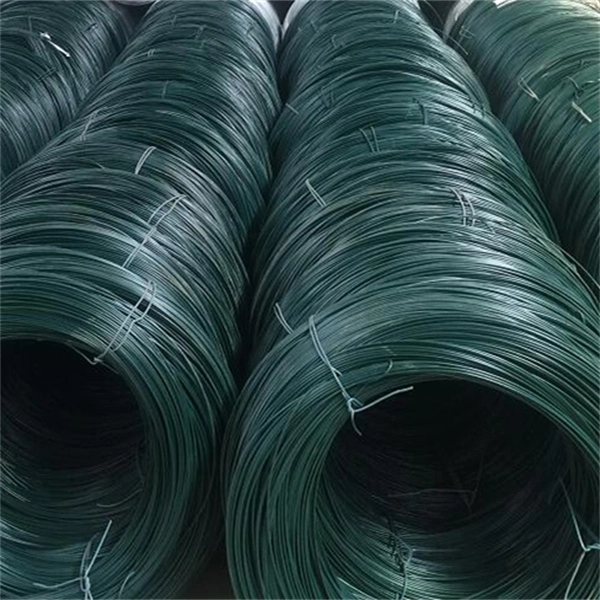
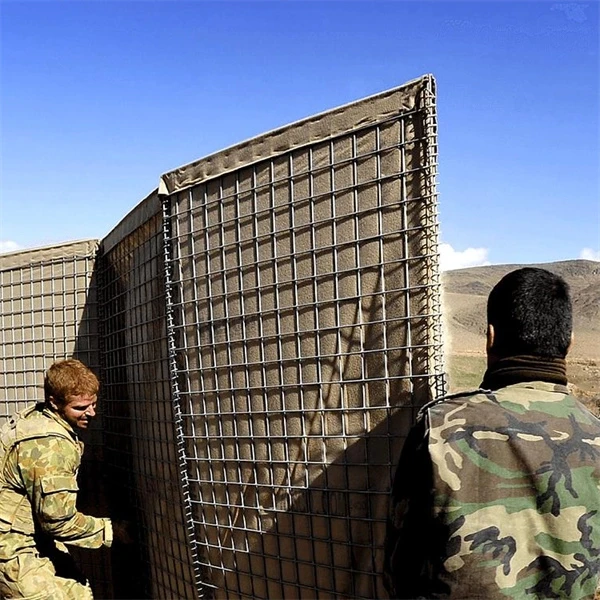
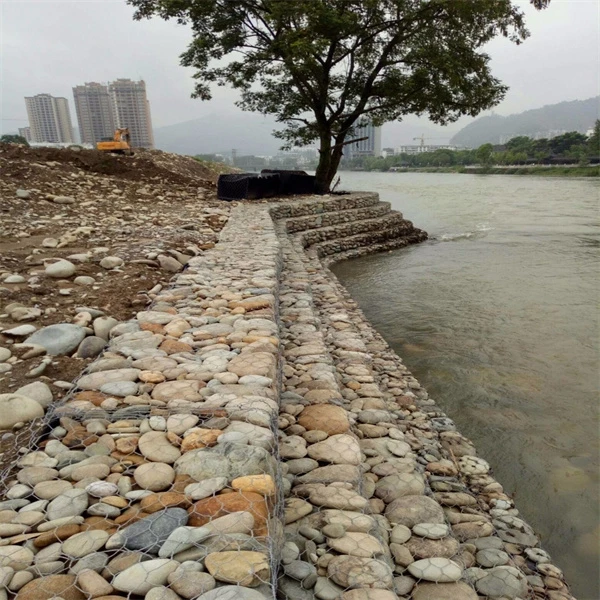
Gabions are a type of containment system designed to hold materials such as stones, rocks, or other aggregates. The word gabion originates from the Italian word gabbione, meaning large cage. These structures are typically made from galvanized steel wire or PVC-coated wire, which enhances their durability and resistance to corrosion. Gabions can be stacked to create walls or filled with rocks to form the foundation for various construction projects.
The Manufacturing Process
Gabion rock factories specialize in the fabrication of these wire mesh structures. The manufacturing process involves several critical steps
1. Wire Mesh Production The first step is the production of wire mesh, which serves as the framework for the gabions. High-quality steel wire is drawn to the required gauge and subsequently woven into a mesh that meets specific engineering standards.
2. Mesh Treatment To ensure longevity, the wire mesh is coated with either zinc or PVC. This treatment protects the metal from environmental factors that can lead to rust and degradation over time.
3. Gabion Assembly After the mesh has been treated, the gabions are assembled into various shapes and sizes. This modularity allows for customization based on project needs. Gabions can be designed as rectangular prisms, cubes, or other configurations.
4. Quality Control As with any manufacturing process, quality control is crucial. Gabion rock factories implement rigorous testing procedures to ensure that the final products meet industry regulations and can withstand structural loads.
5. Logistics and Distribution Once manufactured, the gabions are packaged and transported to construction sites. Efficient logistics are essential to ensure that these materials arrive on time, as delays can affect project schedules.
gabion rock factory
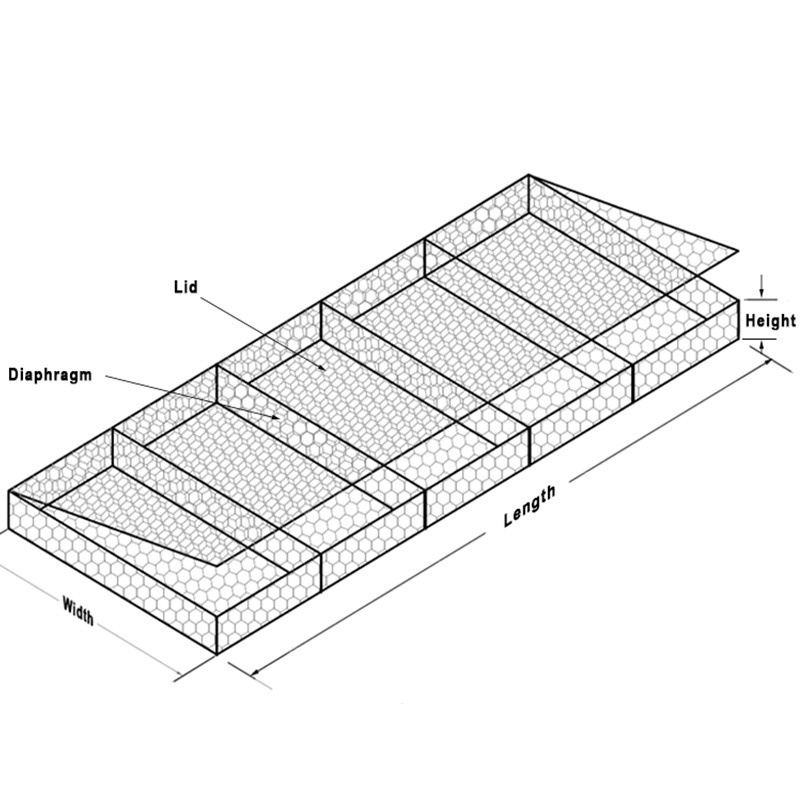
Applications of Gabions
The versatility of gabions is evident in their wide range of applications
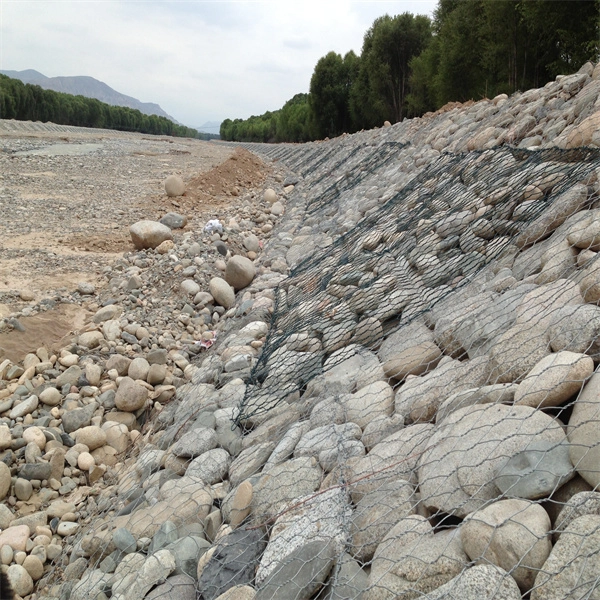
- Erosion Control Gabions are frequently used along riverbanks and coastlines to help prevent erosion. They stabilize soil and absorb the energy of waves or flowing water, mitigating the risk of land loss.
- Retaining Walls In areas with uneven terrain, gabion walls provide sturdy support. Their flexible design allows them to accommodate settling and shifting ground without collapsing.
- Drainage Solutions Gabions can facilitate proper water drainage in landscape design. They allow water to flow through while trapping sediments, thereby improving soil quality.
- Architectural Features In addition to functional uses, gabions can also serve aesthetic purposes. They can be incorporated into landscaping, gardens, and parks, adding a natural yet structured element to the environment.
Environmental Considerations
Gabion rock factories contribute positively to sustainability in construction. The materials used are often locally sourced, reducing transportation costs and environmental impact. Additionally, the use of natural stones promotes biodiversity as gabion structures can provide habitats for various wildlife.
Conclusion
Gabion rock factories are integral to modern construction, providing essential materials that enhance the durability and sustainability of various structures. From erosion control to aesthetic landscaping, the applications of gabions are vast and varied. As the global focus shifts towards sustainable building practices, the role of gabion rock factories is likely to expand, ensuring they remain at the forefront of construction innovation. The future of construction will not only depend on the materials used but also on the methods of production, making gabion rock factories a critical piece in the puzzle of sustainable development.
-
Why PVC Coated Gabion Mattress Is the Best Solution for Long-Term Erosion Control
NewsMay.23,2025
-
Gabion Wire Mesh: The Reinforced Solution for Modern Construction and Landscape Design
NewsMay.23,2025
-
Gabion Wall: The Flexible, Seismic-Resistant Solution for Modern Landscaping and Construction
NewsMay.23,2025
-
Gabion Wall Solutions: The Durable, Decorative, and Affordable Choice for Every Landscape
NewsMay.23,2025
-
Gabion Basket: The Durable and Flexible Alternative to Traditional Retaining Walls
NewsMay.23,2025
-
Gabion Basket: The Proven Solution for Slope Stability and Flood Control
NewsMay.23,2025
-
Versatility of Chain Link Fence Gabion
NewsMay.13,2025






