Nov . 11, 2024 02:48 Back to list
Gabion Drainage Solutions for Effective Erosion Control and Water Management Systems
Understanding Gabion Drainage Systems A Comprehensive Overview
In the realm of civil engineering and landscape architecture, effective drainage systems are crucial for maintaining the integrity of structures and preventing erosion. One innovative solution that has gained popularity is the use of gabion drainage systems. These structures not only serve functional purposes but also enhance the aesthetic appeal of environments in which they are implemented. This article delves into the concept of gabion drainage, its construction process, benefits, and applications.
What are Gabions?
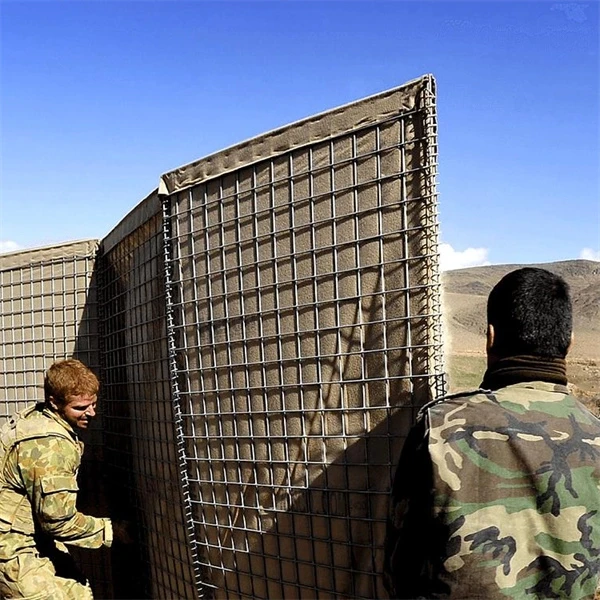
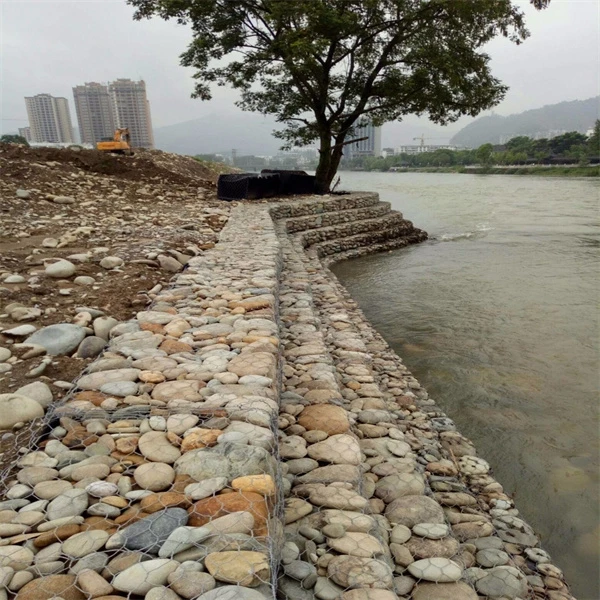
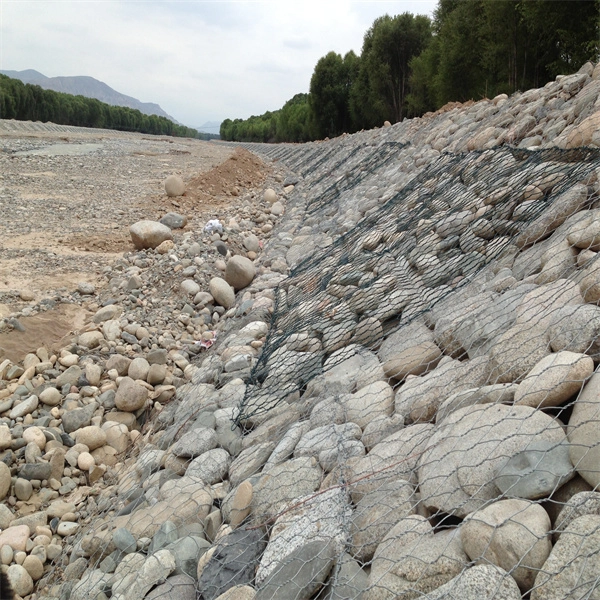
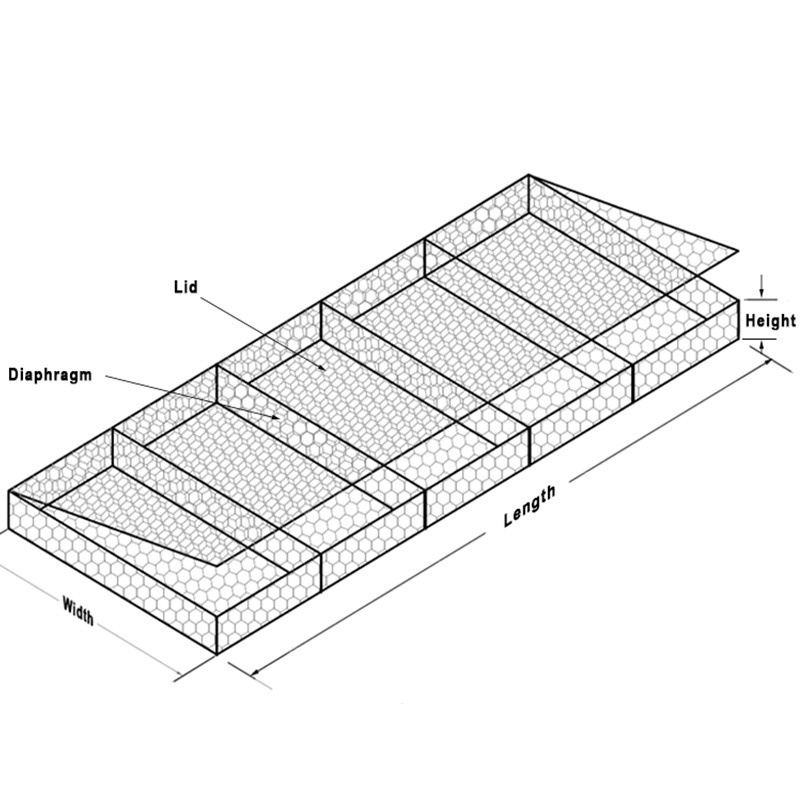
Gabions are wire-bound cages filled with various materials, typically stones, gravel, or soil. Originally used for military fortifications in the 19th century, modern gabions have found their way into environmental applications, particularly in erosion control and drainage systems. Their versatility allows for a range of configurations, which can be tailored to the specific needs of a project.
The Function of Gabion Drainage Systems
Gabion drainage systems integrate the principles of gravity drainage and porous media to effectively manage water runoff. By allowing water to flow through the rocks or other fill materials, gabions prevent the saturation of surrounding soil and reduce the risk of erosion. This is particularly important in areas prone to heavy rainfall or where slopes are susceptible to washouts.
When water passes through the gaps between the stones in a gabion, it is naturally filtered, which minimizes sedimentation in downstream water bodies. This not only protects aquatic ecosystems but also enhances the quality of surface water. Moreover, the structural integrity of the gabions helps to stabilize slopes and retain soil, making them ideal for use in landscaping and construction projects.
Construction of Gabion Drainage Systems
Constructing a gabion drainage system involves several key steps
1. Site Assessment The first step is to evaluate the site where the gabion will be installed. Factors such as soil type, water flow patterns, and existing vegetation need to be considered.
2. Selecting Materials The type of wire used for the gabion cages can vary, but it is typically galvanized or coated to resist corrosion. The fill material, often local stone, should be durable and adequately sized to fit the gabion structure.
3. Building the Framework The gabion baskets are assembled by connecting the wire mesh to create the desired shape and dimensions. The cages must be securely fastened to withstand water flow and pressure.
4. Filling the Gabions Stones or other selected materials are filled into the cages. The filling process must ensure there are no significant gaps, promoting the drainage function.
5. Placement and Integration Finally, the filled gabions are strategically placed in their designated locations. They can be stacked or arranged in various configurations based on design requirements and drainage needs.
gabion drainage factory
Advantages of Gabion Drainage Systems
Gabion drainage systems offer numerous advantages compared to traditional drainage methods
- Cost-Effectiveness The materials used for gabions, especially local stones, can reduce transportation costs and overall expenses
.- Environmental Benefits Gabions can blend seamlessly into the natural landscape, promoting biodiversity and minimizing visual impact. Their design allows for vegetation to grow, further stabilizing the soil.
- Durability and Longevity Gabion structures are known for their resilience. With proper installation and maintenance, they can last for decades without significant degradation.
- Adaptability Gabion drainage systems can be customized to meet specific needs. Whether it’s creating a simple drainage trench or a more complex retaining wall, gabions can be molded to fit various scenarios.
Applications of Gabion Drainage Systems
Gabion drainage systems are versatile and can be applied in a multitude of settings
- Residential Landscapes Used in gardens or driveways to control runoff and prevent flooding.
- Highway Construction Employed alongside roads and highways to manage excess rainwater and prevent erosion.
- Riverbank Protection Effective in reinforcing riverbanks and protecting against flooding while enhancing the habitat for aquatic life.
- Public Parks Used as decorative elements that also serve practical drainage purposes, creating beautiful landscapes that function well.
Conclusion
Gabion drainage systems represent a forward-thinking solution to some of the most pressing challenges in water management and erosion control. Their blend of functionality and environmental compatibility make them an ideal choice for a variety of projects. As awareness of sustainable practices grows, the use of gabions will likely continue to expand, proving that even the simplest structures can provide significant benefits when designed thoughtfully.
-
Visualizing Gabion 3D Integration in Urban Landscapes with Rendering
NewsJul.23,2025
-
The Design and Sustainability of Gabion Wire Mesh Panels
NewsJul.23,2025
-
The Acoustic Performance of Gabion Sound Barriers in Urban Environments
NewsJul.23,2025
-
Mastering the Installation of Galvanized Gabion Structures
NewsJul.23,2025
-
Gabion Boxes: Pioneering Sustainable Infrastructure Across the Globe
NewsJul.23,2025
-
Custom PVC Coated Gabion Boxes for Aesthetic Excellence
NewsJul.23,2025
-
Installation Tips for Gabion Wire Baskets in Erosion Control Projects
NewsJul.21,2025






